Java 8 Predicate花样用法_predicate CSDN博客
In this guide, you will learn about the Predicate test() method in Java programming and how to use it with an example.. 1. Predicate test() Method Overview. Definition: The Predicate.test() method is a functional interface method in Java that is primarily used to test a value and return a boolean result.. Predicate is a part of the java.util.function package and provides a contract for a.

Predicate in Java 8 With Examples TechBlogStation
It seems that what you want is not to store a predicate in a Map. What you want is to be able to store something in a map that is able to create a Predicate
Java 8 Predicate花样用法_predicate CSDN博客
Java Predicates have a functional (abstract) method test (Object) that evaluates this predicate on a given Object. Here's an example of writing a simple Predicate that filters integers based on conditions "greater than", "lesser than". The output will be true because 10 < 18. One more example with Predicate in filter ().

Java 8 Predicate Examples Conditions in JDK 8
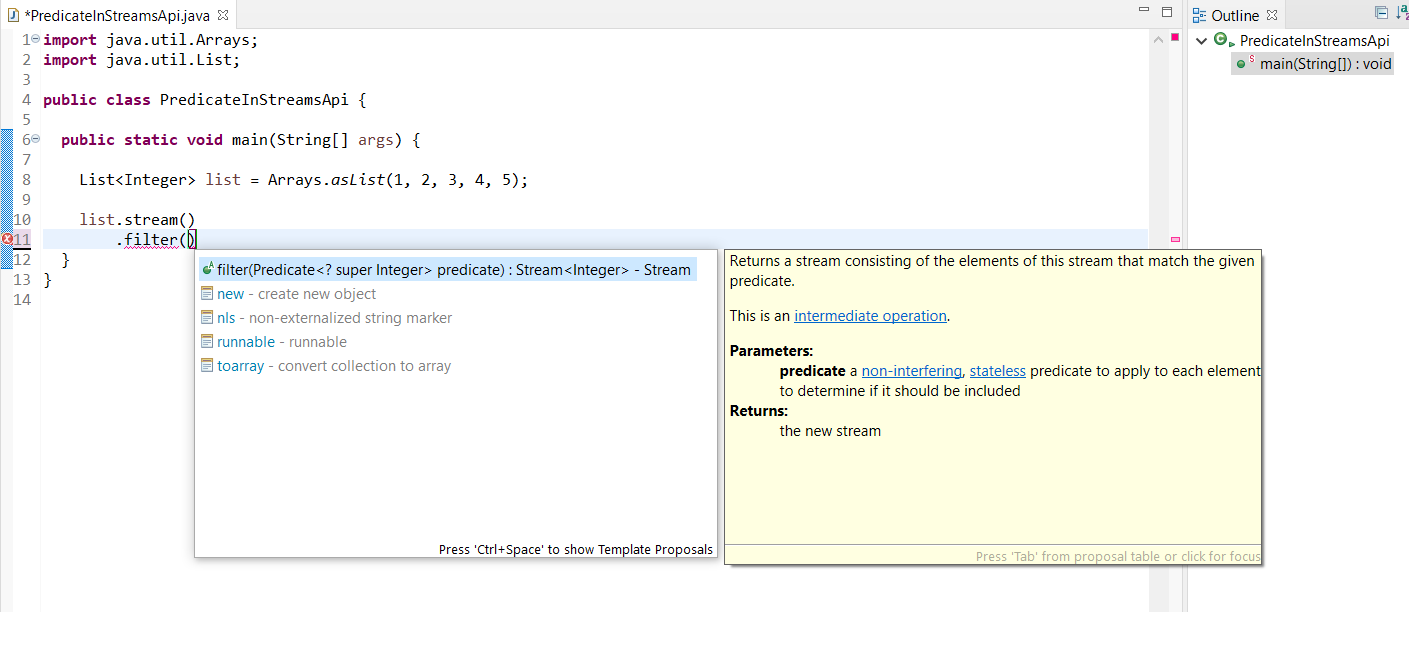
The java.util.function package, employs Predicates to cover the cases where logical tests are to be applied, generically. In general, predicates are used to test something, and return a true or false value according to that test. The predefined functional interface has the structure structure, albeit, accepts a generic parameter: public.

Simplify Your Code with Java Predicate A Comprehensive Guide YouTube
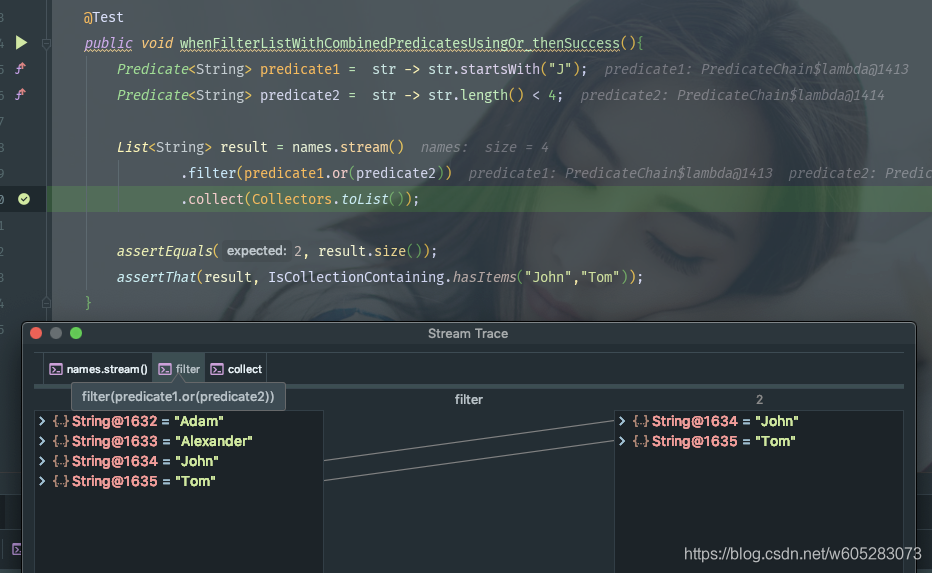
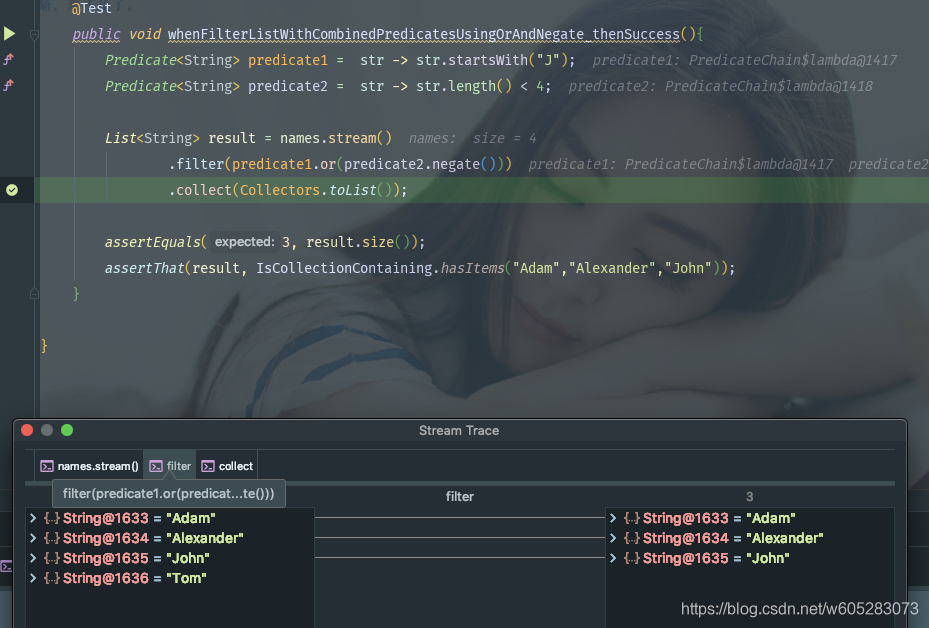
A quick practical guide to Java 8 Predicate Functional Interface with Examples. This is desinged to test the condition. This has a function method test(T t).. Now, We want to add an additional test condition to the existing predicate that name starts with "p". and() method is used to club two predicates and produces a boolean result..

Java 8 Tutorial 04 Predicate functional interface + Generics + Lambda Expressions YouTube
Java 8 Predicate with Examples. Read. Practice. A Functional Interface is an Interface which allows only one Abstract method within the Interface scope. There are some predefined functional interface in Java like Predicate, consumer, supplier etc. The return type of a Lambda function (introduced in JDK 1.8) is a also functional interface.
Tech Trek A Software Engineer's Guide to Code and Beyond Predicates and BiPredicate Functional
Java Predicate Interface. It is a functional interface which represents a predicate (boolean-valued function) of one argument. It is defined in the java.util.function package and contains test() a functional method.
Predicate Interface Java 8 Computer Science java
The java.util.function.Predicate interface contains one abstract method, test(), which takes an object and returns a boolean. @FunctionalInterface public interface Predicate
160 Java 8 Predicate with Examples Java 8 Predicate Examples Predicate java 8
Predicates in Java are implemented with interfaces. Predicate
Predicate Interface Java 8 Computer Science java
Unit Testing Java 8 Predicates. I have a Java 8 Predicate like this. How do I write unit test for this. Predicate

Predicate In Java 8 with examples test(), and(), or(), negate() methods
In Java 8, Predicate is a functional interface, which accepts an argument and returns a boolean. Usually, it used to apply in a filter for a collection of objects. @FunctionalInterface public interface Predicate

Java 8 Predicate example Java2Blog
Interface Predicate

Java 8 Features Part 14 Passing Predicate To A Method YouTube
Let's see some more Java 8 Predicate examples. 1. Employee Filtering: Suppose you have a list of employees and you want to filter out employees who earn more than a certain salary threshold. import java.util.List; import java.util.function.Predicate; public class EmployeeFilterExample { public static void main (String [] args) { List The Predicate interface is part of Java 8 functional programming enhancements.A Predicate is a functional interface and can therefore be used as the assignment target for a lambda expression or method reference.. Implementation-wise, a Predicate is used to pass the behavior (functions) as arguments to methods. In simple words, a Predicate is essentially a boolean-valued function that takes an. Java Predicate. Predicates in Java are implemented with interfaces. Predicate Functional Interface: This is a functional interface and can therefore be used as the assignment target for a lambda expression or method reference. @FunctionalInterface public interface Predicate
Java Predicate

Predicate in Java 8 With Examples TechBlogStation

Java 8 Tutorial 07 Predicate in java 8 Predicate Functional Interface in java 8 YouTube